There are six important type of file header which are given below:-
1)
BITMAPFILEHEADER:-It has the first 14 bytes of any bitmap header.It has the following structure:-
struct bitmapHeader
{
char identity[2];//2bytes
unsigned int sizeOfBmp,//4 bytes
short int reserved,//2 bytes
reserved1;//2 bytes
unsigned int Startingadd;//4 bytes
}
This is the structure for the BITMAPFILEHEADER.In this structure identity is the char array which stores header field which is used to identify the bmp.Possible values are BM,BA,CI etc.Unsigned int sizeOfBmp shows the size of bmp file.Short int reserved & reserved1 are reserved value which actually depends upon application that creates image.The last 4 bytes shows starting address of image data.
2)
BITMAPCOREHEADER:-Its structure has five members
struct bitmapCoreHeader
{
unsigned int sizeOfDib,//4 bytes
widthinPixels,//4 bytes
heightinPixels;//4bytes
short int noOfColorPlanes,//2 bytes
BitsPerPixel;//2 bytes
}
It has some important information like width & height of BMP in pixels & bitdepth of bmp.
3)
BITMAPINFOHEADER:-Its structure has 11 members.It is standard DIB header which we normally use in BMP file.It has total size of 40 bytes.
struct bitmapInfoHeader
{
unsigned int sizeOfDib,//4 bytes
widthinPixels,//4 bytes
heightinPixels;//4bytes
short int noOfColorPlanes,//2 bytes
BitsPerPixel;//2 bytes
unsigned int compressionMethod,//4 bytes
imageSize,//4 bytes
horRes,//4 bytes
verRes,//4 bytes
noOfColorsInColorPalatte,//4 bytes
noOfImportantColorUsed;//4 bytes
}
It have some specific information like compression method used,horizontal & vertical resolution etc.
4)BITMAPV4HEADER:It has following structure:-
typedef struct {
unsigned int bV4Size,//4 bytes
bV4Width,//4 bytes
bV4Height;// 4 bytes
short int bV4Planes,//2 bytes
bV4BitCount;//2 bytes
unsigned int bV4V4Compression,//4 bytes
bV4SizeImage,//4 bytes
bV4XPelsPerMeter,//4 bytes
bV4YPelsPerMeter,//4 bytes
bV4ClrUsed,//4 bytes
bV4ClrImportant,//4 bytes
bV4RedMask,//4 bytes
bV4GreenMask,//4 bytes
bV4BlueMask,//4 bytes
bV4AlphaMask,//4 bytes
bV4CSType;//4 bytes
CIEXYZTRIPLE bV4Endpoints;//36 bytes
unsigned int bV4GammaRed,//4 bytes
bV4GammaGreen,//4 bytes
bV4GammaBlue;// 4 bytes
} BITMAPV4HEADER, *PBITMAPV4HEADER;
It has Red,Green ,Blue & Alpha mask.4bytes for color space type.It also Gamma for all three RGB values
5))BITMAPV4HEADER:-It is the extended version of BITMAPINFOHEADER.It has following structure:-
typedef struct {
unsigned int bV5Size,//4 bytes
bV5Width,//4 bytes
bV5Height;// 4 bytes
short int bV5Planes,//2 bytes
bV5BitCount;//2 bytes
unsigned int bV5V4Compression,//4 bytes
bV5SizeImage,//4 bytes
bV5XPelsPerMeter,//4 bytes
bV5YPelsPerMeter,//4 bytes
bV5ClrUsed,//4 bytes
bV5ClrImportant,//4 bytes
bV5RedMask,//4 bytes
bV5GreenMask,//4 bytes
bV5BlueMask,//4 bytes
bV5AlphaMask,//4 bytes
bV5CSType;//4 bytes
CIEXYZTRIPLE bV5Endpoints;//36 bytes
unsigned int bV5GammaRed,//4 bytes
bV5GammaGreen,//4 bytes
bV5GammaBlue,// 4 bytes
bV5Intent,// 4 bytes
bV5ProfileData,// 4 bytes
bV5ProfileSize,// 4 bytes
bV5Reserved;// 4 bytes
} BITMAPV5HEADER, *PBITMAPV5HEADER;





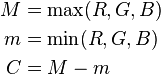


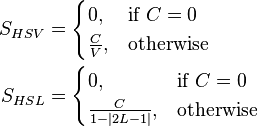




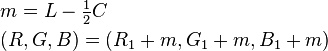



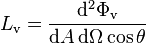
 is the luminance (
is the luminance ( is the
is the 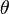 is the
is the  is the
is the 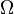 is the
is the 